DIEP flap breast reconstruction is the most advanced form of breast reconstruction that can be offered today. The terminology “flap” in plastic surgery refers to any tissue that is moved around on a body. DIEP flap stands for Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator flap and it is named after the blood vessels that are harvested with the tissue to keep the tissue alive. This form of reconstruction is ideal for patients who have an adequate amount of abdominal skin and fat. Instead of implants, this abdominal flap is used to reconstruct the breast. Traditional abdominal-based flap techniques, such as the transverse rectus abdominal myocutaneous (TRAM) flap, sacrificed the entire six-pack muscles. Advances in microsurgery have evolved the TRAM flap into the DIEP flap where specialized trained microsurgeons can now spare the transfer of abdominal muscles – decreasing the high complications of bulges, hernias, and loss of abdominal strength that are frequently seen in the TRAM or free-TRAM operation.
Best Candidates for DIEP Flap
DIEP flap is perfect for patients who are seeking a more natural-looking, soft set of breasts. Patients who elect to only have a unilateral (one-sided) mastectomy will have a better match with a DIEP flap since it replaces “like” with “like”. Symmetry is harder to achieve with an implant and a natural breast since you comparing apples and oranges. DIEP flaps are indicated in patients with a history of radiation since radiated tissue with an implant placed is fraught with complications. Unfortunately, those patients who have had a tummy tuck or extensive abdominal surgery may not be candidates for DIEP flap reconstruction.
DIEP Flap Surgery
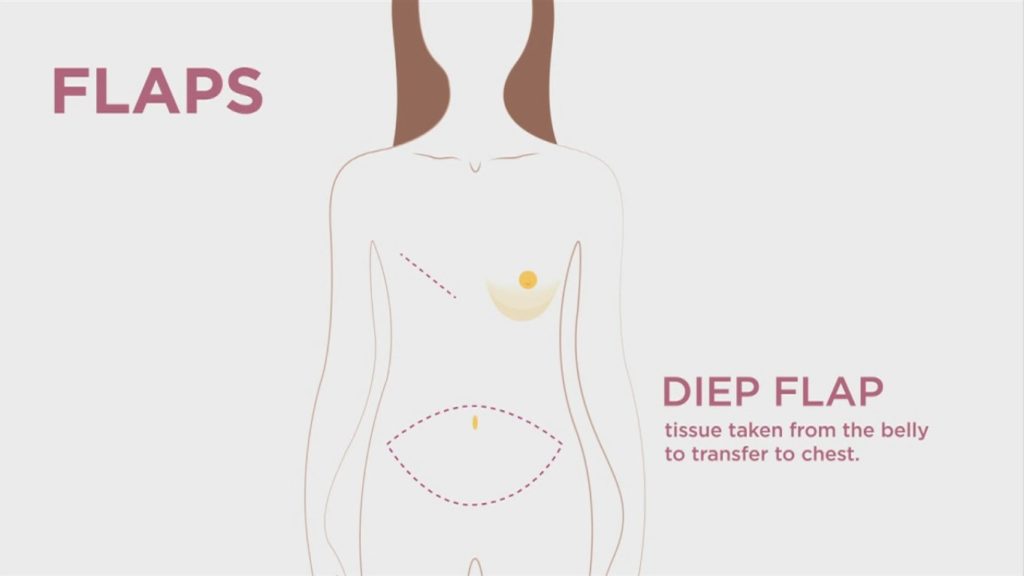
The tissue that is utilized to reconstruct the breast in the DIEP flap is from the lower abdomen. Good candidates for this surgery are usually women in their later years who exhibit stubborn unwanted loose skin and fat in the lower abdomen after pregnancies. This is typically the same tissue that is discarded in a tummy tuck but instead, harvested with a pair of blood vessels and transplanted to the chest. The surgery is similar to a transplanted kidney in that the tissue is completely disconnected and then reconnected. 30-60 minutes of the surgery is performed under the microscope where the blood vessels are reattached with suture finer than a human hair. It is different from a kidney or lung transplant in that no anti-rejection medications are required since the tissue is from the same donor. The abdominal tissue can be used to reconstruct one breast or two breasts provided there is enough skin and fat. Immediate reconstruction (at the same time as mastectomy) will offer the best cosmetic results, however, the surgery is also often done in a delayed fashion (after the mastectomy) where there is no breast present and a flat chest wall.
The surgery typically takes anywhere between 4-12 hours depending on the level of experience of the surgeon and the variations in individual patient anatomy (some more straightforward and some more difficult). At Memorial Plastic Surgery, we perform the surgery with two board-certified microsurgeons to complete the reconstruction in a more efficient and timely fashion. The surgery will take 2-4 hours for one breast and 4-6 hours for both breasts.
DIEP Flap Recovery
The average recovery time for DIEP flap patients is between 4 – 6 weeks. Soreness around the breast and abdominal areas is normal and will eventually subside throughout the recovery period. By two weeks, patients are 80-90% back to normal. Desk jobs and normal activities can be resumed 5 to 6 weeks after the procedure. Surgical drains are also needed after DIEP flap surgery to avoid blood and fluid accumulation. These are placed underneath the skin and tissues at each incision site. Most of the time, 1 drain is placed into each breast and two in the abdomen. Although the DIEP flap is living breathing tissue, the DIEP flap does not restore nipple and breast sensation loss. The light sensation is always gained after years of healing.
One rather infrequent complication of DIEP flap reconstruction involves clots (thrombosis) in the pair of blood vessels that are reconnected. Although that portion of the surgery is delicately and meticulously performed under the microscope, there can still be the potential for clot formation. Formation of a clot will lead to loss of blood flow into or out of the flap. The nurses in the hospitals carefully monitor this risk of thrombosis over the 3-5 day hospital stay. A clot or thrombosis is treated with immediate re-operation to attempt to restore normal blood flow. The clot risk at Memorial Plastic Surgery is around 2 percent.
Questions to Ask Your Surgeon
- Am I a good candidate for a DIEP Flap breast reconstruction?
- How will my reconstructed breast compare with my other breast unaffected by cancer?
- What are the risks associated with the DIEP Flap?
- How long will the results of my DIEP Flap surgery last?
- Does my plastic surgeon have any microsurgery training?
- How many DIEP flaps does the plastic surgeon or practice do every month? Year?
- What is the thrombosis (or clot rate) of the DIEP flaps in the practice?
- What is the success rate of DIEP flaps for the surgeons in the practice?